New solution for Millable rubber molding
- Sodick's stuffer box, changing rubber supply -
Millable rubber molding to handle increasing demand for injection molding
Liquid Injection Molding (LIM) with materials such as liquid silicone rubber mixes two liquid materials just before molding as shown below at right. However, millable rubber molding uses a single material with a long storage life. Many of the millable rubber products are manufactured using a compression molding method, an open-type system that resembles a waffle iron, into which rubber cut to a predetermined weight is put in the mold then pressurized to form products.
However, in recent years, the application of the injection molding method which is suitable for closed processes right from material input through to product removal is under consideration, and demand is increasing. Reasons for this are efforts to increase automation and increase labor savings, along with its low cost and high strength when compared to liquid materials, the development of high-speed vulcanization materials, and its suitability for small-lot production.
Sodick has also applied the V-LINE® injection and weighing system as well as its molding technology previously built with LIM to this millable rubber molding process in order to improve productivity and the reliability of product quality.

Molding issues with millable rubber and air mixture
Millable rubber is thick—similar to clay or putty, and cannot be pressure fed with a dosing pump as with liquid materials. Additionally, the material is kneaded into thin sheets using rollers, and then formed into bullet shape for molding. This kneading and forming of the material introduces air as shown at the top right.
When processing typical millable rubber molded parts such as connector waterproof seals that have complex wavy cross-sections, these cannot have air vents in the optimal position in the mold. In these cases, even if the mold is vacuumed, a small amount of air may remain at the tip of the molded part, meaning this part is unfilled.
If the structure of the mold does not allow for an overflow, simply vacuuming the mold alone will be unable to solve the problem of unfilled products resulting from air traps (air mixture and unfilled products due to air entrapment).
In addition, lowering the mold temperature as a measure to prevent unfilled molds means more time is required for vulcanization, leading to a delay in cycle time and lower productivity.

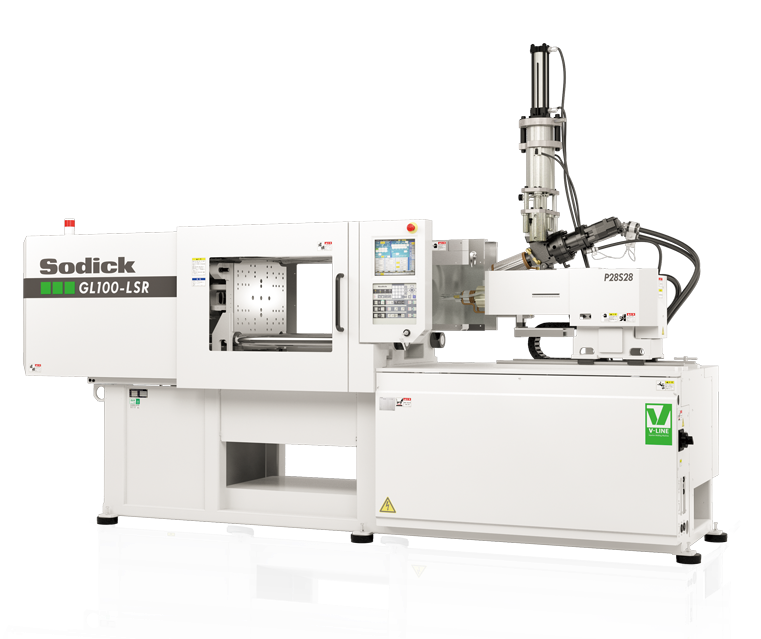
Sodick's LSR Series of injection molding machines for thermosetting resin
Sodick's proprietary V-LINE® injection molding machine lineup includes the LSR Series, which is optimized for thermoset resin molding.
By jointing or mounting a dosing pump for supplying liquid material and a stuffer box for supplying millable rubber supply to the machine to the feed section of the molding machine, the machine can perform molding of low- to high-viscosity thermoset resins.

Sodick's stuffer box (material supply device)
The stuffer box is a special device that supplies the injection molding machine with millable rubber in a bullet shape, and its operation is coupled to the injection molding machine.
Since millable rubber is highly viscous, it is difficult to first remove the air contained in the material using a degassing device or similar. If this air remains and enters the mold, this becomes an air trap, and the air cannot be removed solely by degassing (vacuuming) the mold.
Sodick has developed a new stuffer box with vacuum degassing functionality incorporating the ability to perform vacuum degassing before the material is supplied to the injection molding machine.
Stuffer box Lineup
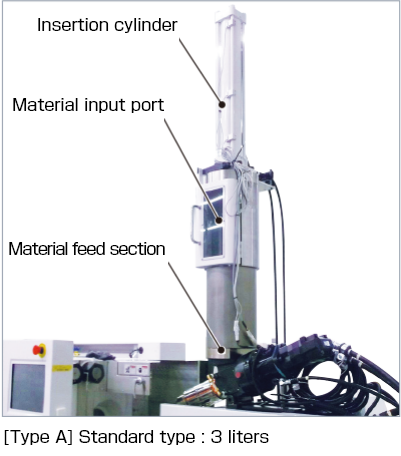
Sodick offers a lineup comprising the Type A for standard material insertion
and the Type B that incorporates degassing functionality.
Type AStandard type
Offers high-quality, high-productivity millable rubber molding
Standard-type stuffer box incorporated into the material feed section of the LSR Series horizontal injection molding machines, and that pushes the millable rubber into the feed screw.
High thrust insertion cylinder for high viscosity materials. Two sizes are available to match supply volumes: 3 liters and 9 liters.
Specifications
| Applicable types (screw diameter) | GL60-LSR (S28 mm) GL100-LSR GL150-LSR (S28 to S40 mm) |
|---|---|
| Input material capacity | 3, 9 liters |
| Applicable material hardness | Shore A50 or less |
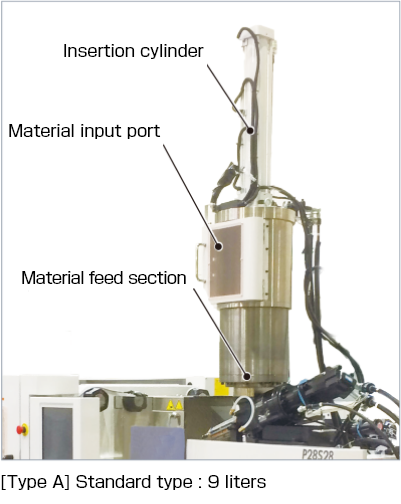
Type BDegassing type
"Low air volume material supply" reduces air traps in molded parts
This is a newly developed degassing mechanism specification for the LSR Series of horizontal injection molding machines. Type A: Enables material supply with less air content than the standard type. This significantly reduces the amount of air traps that previously could not be solved through mold vacuuming. Die plate conversion method to match material characteristics.
Specifications
| Applicable types (screw diameter) | GL60-LSR (S28 mm) GL100-LSR GL150-LSR (S28 to S40 mm) |
|---|---|
| Input material capacity | 3 liters |
| Applicable material hardness | Shore A50 or less |
| Ultimate vacuum | 0.1 hPa (separate vacuum pump required) |

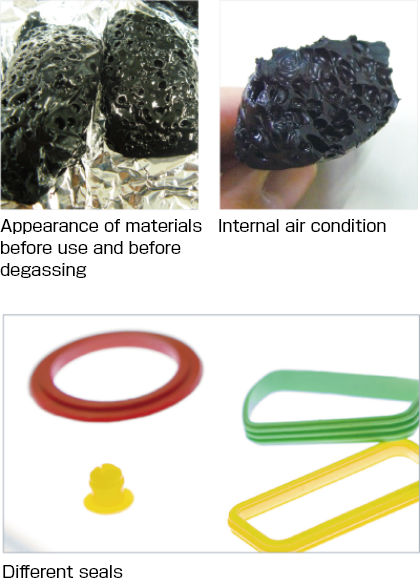
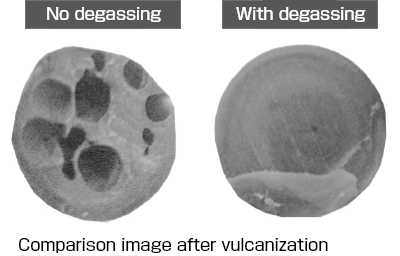
Effectiveness of the degassing function
The images on the right show an enlarged comparison of materials after vulcanization with and without degassing.
If vulcanization is carried out without injection into the mold, it is clear that without degassing, the product has hardened with large air bubbles. However with degassing, these air bubbles are not visible.
Solution using a stuffer box with degassing function
- High density material filling
 Reduced vulcanization time (hardening time)
Reduced vulcanization time (hardening time)- Simplified mold vent construction
 Reduced frequency of mold maintenance
Reduced frequency of mold maintenance- Use of high air content materials
 Enhanced molding quality
Enhanced molding quality- Increased productivity (reduced cycle time)
 Reduced mold production costs
Reduced mold production costs- Reduced mold maintenance costs
 Reduced material forming cost (permissible air mixture)
Reduced material forming cost (permissible air mixture)


